Fish Oil to Cure Cancer? Professor Sees Promise in Store-Bought Product
While many cancer researchers focus their work on exotic compounds and toxic chemicals, Jahan Abdi is looking in a different direction: fish oil.
Specifically, it’s EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil pills sold at supermarkets and nutritional stores, that interest Abdi, an assistant professor of clinical laboratory science at CSUDH. “I was very interested in exploring the anti-cancer effects of food-related items, which are not chemical and are not synthesized, so they don’t have the complications of drugs manufactured by a pharmaceutical company,” he said.

Various clinical trials have shown that combining these fish oil components with certain anti-cancer drugs will increase the efficiency of those drugs. But Abdi thinks fish oil components “could be very effective as a monotherapy as well”—that is, as the only treatment needed.
Abdi began his research on fish oil as a PhD student at Utrecht University in the Netherlands. He’s already published a study that found EPA and DHA can kill blood cancer cells while leaving healthy blood cells alone. That could open the door to other possible avenues of study. “If the effects are not specific to a certain kind of cancer, then these components can be included with any cancer treatment,” he said.
Abdi also actively engages undergraduate CSUDH students in his research, starting with training on handling biohazards. They also practice using equipment like a biosafety hood and inverted microscope when growing, monitoring, and treating cancer cells.
“It helps them expand their knowledge, enhance their skills, and learn how to approach a scientific question. They get to know new instruments and advanced technology which will prepare them for real-world clinical experience.”
Get to Know the Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Fish oil isn’t snake oil—the ingredients in this health supplement have been linked to improvements across a variety of ailments, such as heart disease, cardiovascular illness, autoimmune sicknesses, depression, and cognitive decline like dementia and Alzheimer’s. There are two main omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil that scientists credit with positive effects across so many areas of health: EPA and DHA.
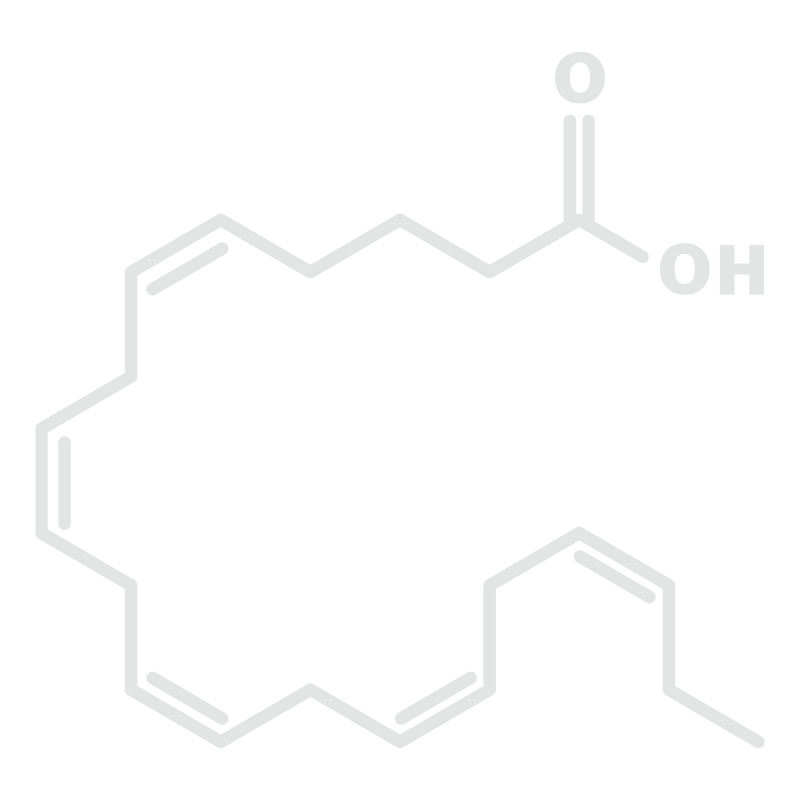
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
The 22 carbon atoms in this fatty acid make it a “long chain” molecule. It plays a key role in the central nervous system, helping supply other nutrients to the brain. Some studies have found a link between higher levels of DHA and lower likelihood of dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and other cognitive decline associated with aging.
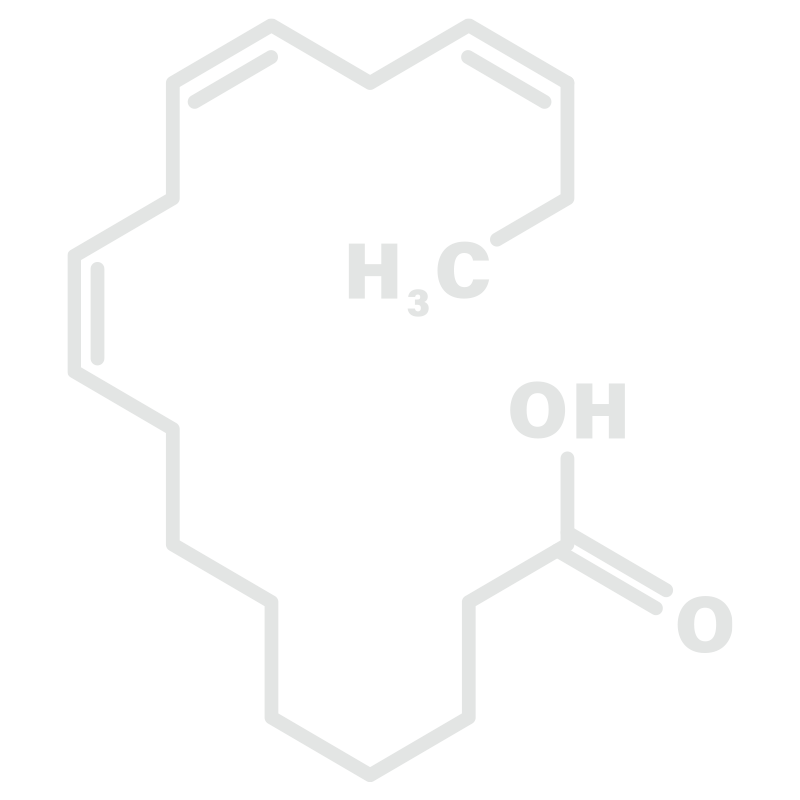
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
EPA is typically linked with DHA, its fatty acid partner in fish oil pills. When taken alone, it can be part of a treatment for high levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream. It has also been used to reduce symptoms of depression.
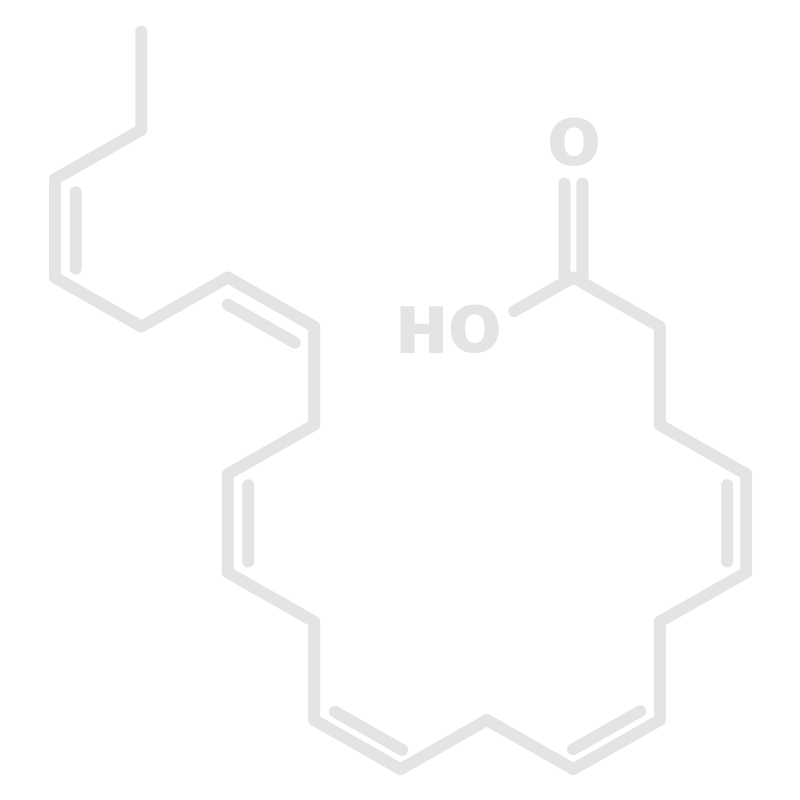
Alphalinolenic Acid (ALA)
This omega-3 comes from plant sources, like nuts, seed and vegetable oils, or berries—blueberries, cranberries, raspberries, and lingonberries. ALA is converted into EPA and DHA inside the body, but only at a very low levels. Like the others, its consumption is linked with improved heart health.



